In a period characterised by swift technological advancements, globalised supply chains, and constant pressure for efficiency, the manufacturing industry has transformed beyond recognition. Companies that once relied on spreadsheets, legacy software, and manual processes now require integrated, real-time systems that orchestrate production from raw materials to final delivery. This is where manufacturing ERP systems step in — serving as the digital backbone that keeps modern factories synchronised, agile, and competitive. This article explores the role of manufacturing ERP systems, their modules, benefits, industry applications, and how businesses can select the right platform for long-term success.
What Are Manufacturing ERP Systems?
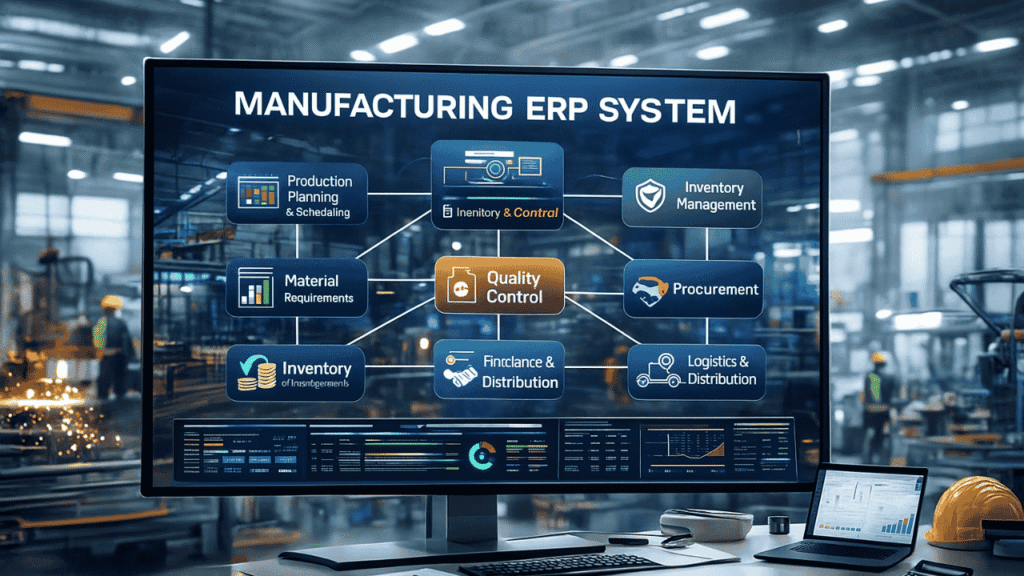
Manufacturing ERP systems (Enterprise Resource Planning systems tailored for manufacturing) are comprehensive software platforms that manage and integrate all functions within a manufacturing organisation. Unlike traditional ERP software that focuses broadly on finance and enterprise functions, manufacturing ERP systems are engineered specifically for production workflows.
Core areas they connect include:
- Production planning and scheduling
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
- Inventory and warehouse management
- Procurement and supplier coordination
- Shop floor execution
- Quality control
- Logistics and distribution
- Finance, costing, and reporting
By consolidating all these operations into a single central system, manufacturers gain real-time visibility, reduce errors, and optimise their end-to-end processes.
Why Manufacturing ERP Systems Matter Today
The modern manufacturing environment faces unique challenges:
- Volatile demand and changing customer expectations
- Shorter product life cycles
- Complex global supply chains
- Labour shortages and skill gaps
- Increasing regulatory and quality requirements
- Pressure for sustainability and waste reduction
Manufacturing ERP systems address these challenges by enabling:
Real-Time Decision Making
Leaders can see instantly what is happening on the shop floor, whether materials are ready, and how operations align with demand forecasts.
Seamless Data Flow
No more disjointed systems or duplicate data entry — ERP creates a single source of truth.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud-based systems especially allow companies to scale as they grow, add new plants or products, and remain future-ready.
Key Features of Manufacturing ERP Systems
Not all ERP systems are created equally. The strongest manufacturing ERP systems typically include a suite of integrated modules that support both tactical and strategic functions. Here are the core ones:
Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
MRP is the foundation of manufacturing planning. It helps manufacturers determine:
- What materials are needed
- When they are needed
- How much to order
MRP ensures optimal inventory levels, preventing costly stockouts or overstocking.
Production Planning & Scheduling
With real-time production data, ERP systems can generate accurate schedules that account for:
- Machine availability
- Labor requirements
- Routing and work centres
- Lead times
This results in higher throughput and reduced downtime.
Inventory & Warehouse Management
Manufacturing ERP systems track every component and finished product with precision:
- Lot and serial tracking
- Automated replenishment
- Barcode/RFID support
- Multi-warehouse visibility
This boosts fulfilment speed and accuracy.
Shop Floor Control
This module connects directly to machines and operators, enabling real-time tracking of:
- Work orders
- Labor hours
- Equipment status
- Production output
- Downtime reasons
It turns the factory floor into a quantifiable, optimised environment.
Quality Management
Quality is central to the manufacturing process. ERP systems incorporate:
- Inspection plans
- Corrective and preventive actions (CAPA)
- Non-conformance tracking
- Compliance documentation
- Traceability for recalls
This ensures consistency and regulatory alignment.
Procurement & Supplier Management
Manufacturers depend heavily on supplier reliability. ERP systems manage:
- Purchase orders
- Vendor performance analytics
- Lead time monitoring
- Contract compliance
Result: better supplier relationships and reduced disruptions.
Financials & Cost Accounting
No manufacturing operation is complete without accurate costing. ERP systems support:
- Job costing
- Standard vs. actual costs
- Cost variance analysis
- Full accounting suite (AR/AP/GL)
Manufacturers gain financial transparency and strategic insight.
Benefits of Implementing Manufacturing ERP Systems
When deployed correctly, manufacturing ERP systems deliver transformative results, both operationally and financially.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
By automating manual processes and connecting departments, ERP reduces delays, increases throughput, and improves team coordination.
Lower Operational Costs
Inventory waste, production errors, and poor scheduling can be costly. ERP systems minimise these by enabling precision planning.
Better Customer Satisfaction
Accurate forecasting, dependable delivery dates, and higher product quality translate into happier customers and stronger loyalty.
Strengthened Compliance and Traceability
Many industries — such as food, chemicals, automotive, and aerospace — require strict traceability. ERP systems document every step effortlessly.
Data-Driven Strategy
From forecasting to financial planning, manufacturing ERP systems turn raw data into strategic action, empowering leaders to stay ahead of competitors.
Industries That Benefit Most from Manufacturing ERP Systems
Manufacturing ERP systems are versatile yet deeply specialised, making them valuable across multiple sectors.
Discrete Manufacturing
Examples: automotive, electronics, machinery
Focus: BOM management, routing, job costing
Process Manufacturing
Examples: chemicals, food & beverage, pharmaceuticals
Focus: recipe/formula management, batch production, compliance
Mixed-Mode Manufacturing
Examples: plastic moulding, packaging, consumer goods
Focus: flexible production types, multi-stage workflows
Make-to-Order & Engineer-to-Order Industries
Examples: custom machinery, fabrication shops
Focus: configuration, advanced scheduling, project costing
How to Choose the Right Manufacturing ERP System
With dozens of ERP vendors available, selecting the right system can be complex. Here’s a structured approach for manufacturers evaluating options:
Identify Your Specific Manufacturing Mode
Are you discrete, process, batch, engineer-to-order, or mixed-mode?
ERP systems often specialise—choose one aligned with your production type.
Evaluate Deployment Options
- Cloud ERP: Scalable, accessible, lower upfront cost
- On-premise ERP: More control, higher initial investment
- Hybrid: Blends both worlds
Most modern manufacturers choose the cloud for its agility.
Assess Essential Integrations
Your ERP should easily connect with:
- MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems)
- CRM
- IoT / machine sensors
- BI/analytics tools
- E-commerce or EDI systems
Integration reduces manual work and increases automation.
Examine Customisation vs. Configuration
A highly customizable ERP may sound appealing, but it can lead to:
- Longer implementation
- Higher maintenance costs
- Difficult upgrades
Prefer systems that offer strong configuration capabilities with minimal coding.
Verify Vendor Expertise in Manufacturing
Choose vendors with proven case studies, manufacturing clients, and strong post-implementation support.
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
TCO includes:
- Licensing
- Hardware (if on-premise)
- Implementation
- Training
- Ongoing support
- Customizations
A cheaper upfront system may become more expensive in the long term.
The Future of Manufacturing ERP Systems
The ERP landscape is evolving rapidly. The next decade promises enhancements such as:
AI-Driven Automation
Predictive maintenance, intelligent scheduling, and automated quality checks.
IoT-Enabled Smart Factories
Machines feed real-time data into ERP for fully connected operations.
Advanced Analytics & Digital Twins
Simulating entire production environments before making changes.
Greater Personalization
More industry-specific versions of ERPs with prebuilt best-practice workflows.
Sustainability Tracking
Carbon footprint measurement, waste analytics, and regulatory reporting.
Manufacturers adopting ERP now are positioning themselves for these future innovations.
Conclusion
Manufacturing ERP systems have become indispensable tools for companies striving to remain competitive in a complex industrial landscape. By integrating every facet of production — from materials procurement to financial reporting — ERP systems create a unified, efficient, and data-driven organisation. Whether you’re a small fabrication shop or a global manufacturer with multiple plants, the right ERP system can transform operations, boost profitability, and unlock new levels of agility.
You May Like: Portsdown Technology Park: A Hub of Innovation and Defence Excellence in the UK